When Tesla announced its total deliveries in early September, initial numbers fell short of investors’ expectations, raising concerns over the vehicle’s launch performance. However, Tesla soon surprised the market by announcing that the Cybertruck had already achieved positive gross margin—a significant milestone for a vehicle so radically different from any truck before it. The Cybertruck’s unique design and manufacturing requirements demanded an unprecedented level of innovation and execution.
Despite the challenges of pioneering new manufacturing techniques and applying first-principles thinking, Tesla has managed to bring the Cybertruck to market profitably, setting a new standard for innovation and financial discipline. In this blog, I’ll explore the key factors that enabled Tesla to achieve gross profit so quickly, examining the groundbreaking strategies in design, manufacturing, and pricing that make the Cybertruck a financial success. As other so called ‘EV automaker’ face production cuts and softening demand, Tesla’s early success with the Cybertruck demonstrates its resilience and ability to turn visionary concepts into profitable reality.

1. Gigacasting: A Game-Changer for Tesla’s Cybertruck
The first reason Tesla managed to generate positive gross margin so quickly for the Cybertruck lies in its innovative use of gigacasting for manufacturing key parts of the vehicle. Tesla employs a Gigapress, which injects molten aluminum into a Gigapress cold chamber to produce large sections of the car’s underbody—both the front and rear—in a single casting. This process uses up to 9,000 tons of clamping pressure to die-cast these critical sections, a move that revolutionizes how underbodies are built.
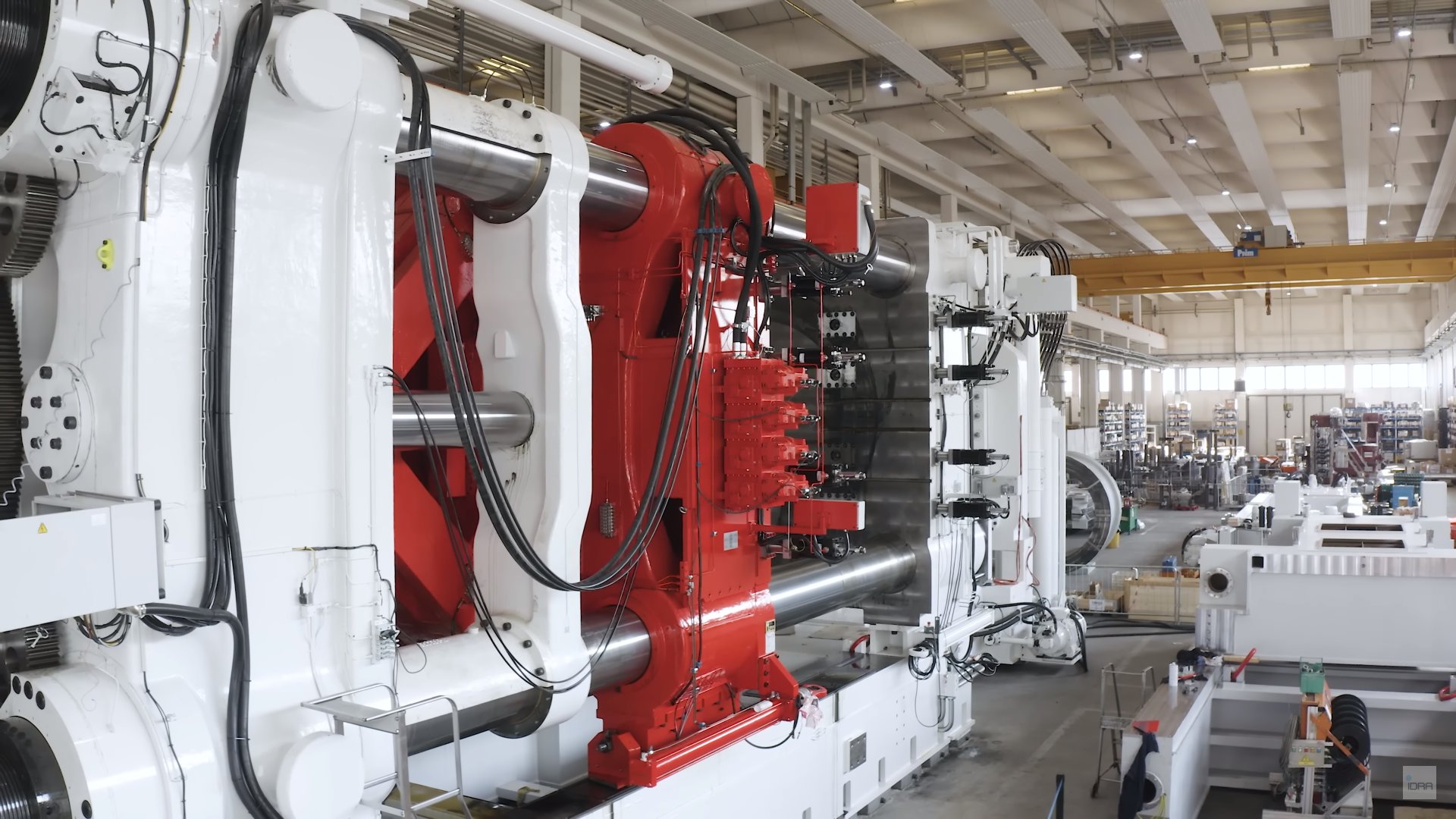

In a conventional vehicle, the underbody consists of hundreds of individual parts that must be welded, joined, and assembled, a process that consumes both time and labor. Tesla’s gigacasting approach minimizes this complexity by reducing hundreds of parts to a single piece. This method cuts labor costs, saves on materials, and accelerates production, allowing Tesla to ramp up Cybertruck deliveries more quickly.
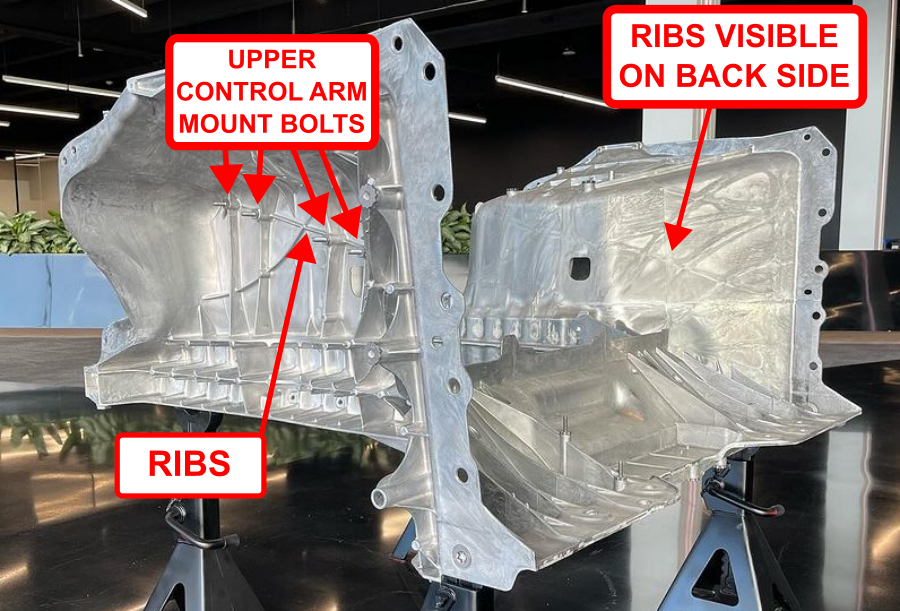
A single-piece gigacasting forms the Cybertruck’s entire front end, with a similar gigacast used for the back end as well.
Most companies shy away from gigapressing due to the substantial initial investment and the departure from traditional manufacturing methods. However, Tesla takes a first-principles approach, rethinking truck manufacturing from the ground up, rather than adhering to legacy industry standards. This allows Tesla not only to introduce unique designs like the Cybertruck’s but also to create a streamlined and efficient production process, supporting faster cash flow generation.
2. First-Principles Design and the Exoskeleton
Another reason for Tesla’s ability to achieve rapid positive gross marin with the Cybertruck lies in its groundbreaking first-principles design approach. Rather than adhering to traditional truck manufacturing methods—such as the conventional body-on-frame design used for over a century—Tesla reimagined how a truck could be built by questioning each design choice from the ground up.
In a typical truck design, a body-on-frame structure is standard, where a steel frame carries the load, and the truck body sits on top as a non-load-bearing component. This setup, while durable, adds unnecessary weight due to the non-load-bearing body, impacting the vehicle’s overall efficiency. Tesla challenged this long-standing design by asking, How would we build a truck if we had never seen one before?
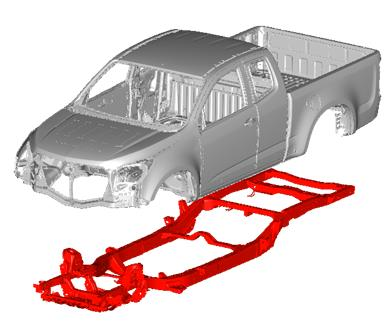
Truck with a body-on-frame design, where the frame is load-bearing, and the body is non-load-bearing.
With the Cybertruck, Tesla combines the strengths of both traditional and unibody designs through an innovative exoskeleton. The exoskeleton not only serves as the external structure but also acts as the load-bearing framework. Inspired by truss structures, like those seen in the Eiffel Tower or steel bridges, the exoskeleton features a triangular design that distributes impact and load efficiently across the entire frame, enhancing durability.
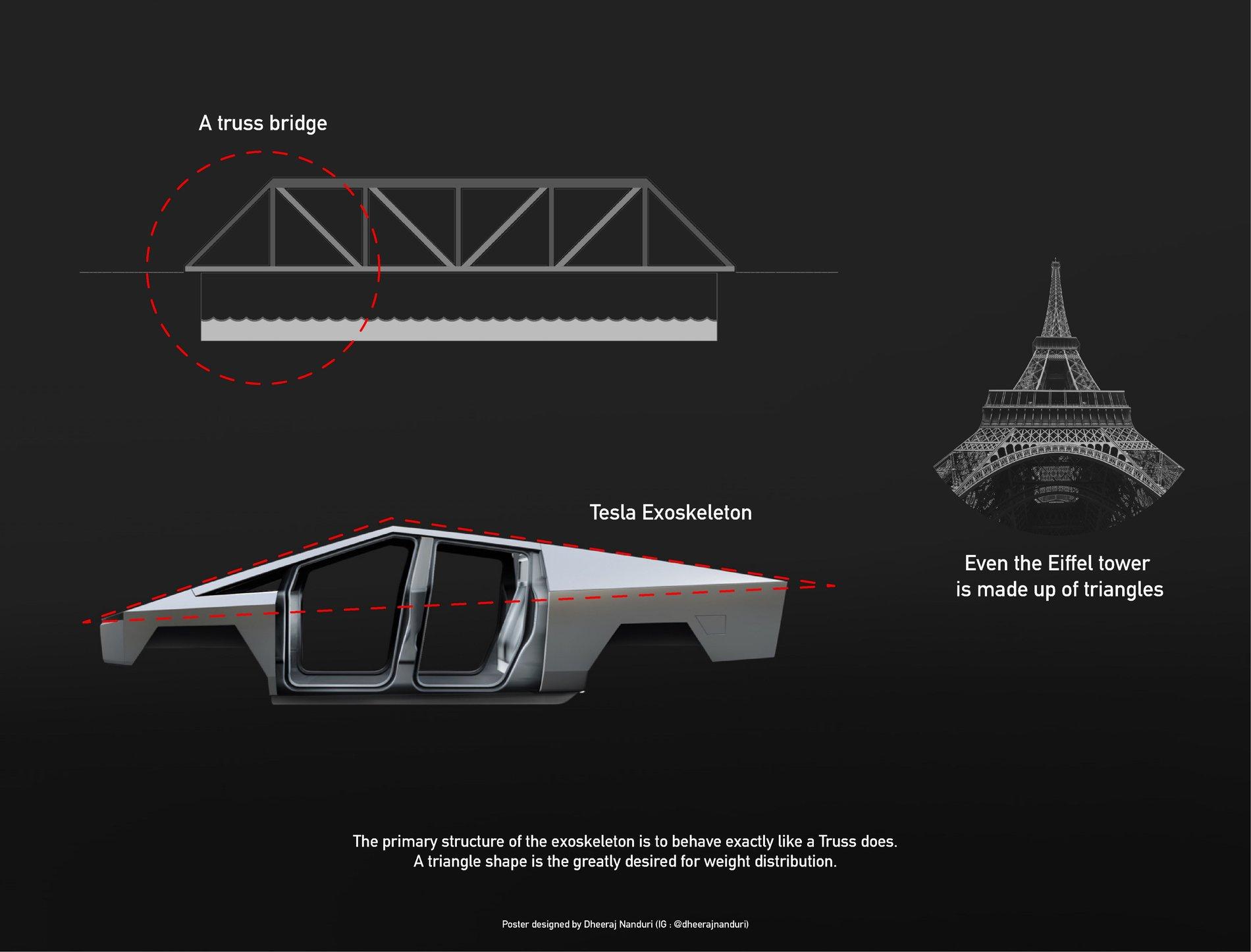
Unlike unibody designs—where the internal frame bears the load and exterior panels remain non-load-bearing—the Cybertruck’s exoskeleton consolidates both function and form. This approach eliminates the need for additional weight in non-load-bearing body components, making the truck lighter and structurally more resilient. The exoskeleton directly supports the car’s weight and provides a strong, impact-resistant exterior without added, purely aesthetic panels.
Through this first-principles design, Tesla not only optimizes the Cybertruck’s durability but also simplifies its production process, leading to faster manufacturing times and cost savings. This pioneering approach ultimately supports Tesla’s ability to generate positive gross profit quickly by reducing unnecessary materials and assembly steps, a significant advantage over traditional truck manufacturing methods.
3. Foundation Series Pricing Strategy: A Key to Early Gross Profit
When Tesla launched the Cybertruck’s first deliveries, they did so with the Foundation Series, priced significantly higher than a typical truck—starting from $100,000. This premium model included full self-driving capabilities and other high-end features, appealing to early adopters eager for Tesla’s groundbreaking truck design. Even at a higher price point, demand for the Foundation Series was off the roof, fueled by the Cybertruck’s unique look and enthusiastic endorsements, including celebrity shout-outs on social media. This organic advertising created a buzz and solidified the Cybertruck’s status as a desirable, futuristic vehicle.

During the initial ramp-up phase, production costs are typically high, as Tesla refines the manufacturing process to scale efficiently. By pricing the Foundation Series at a premium, Tesla was able to offset these early, high production costs and stabilize gross profit, even before reaching full production capacity. This strategy provided Tesla with the financial cushion needed to overcome the costly ramp-up period, allowing them to generate positive gross margin from the outset.
As of now, Tesla has shifted from the Foundation Series to the standard Cybertruck, priced at around $80,000 for a basic dual-motor. However, the initial Foundation Series sales played a critical role in funding the ramp-up and supporting Tesla’s early positive gross profit goals.
4. Battery Innovation: The 4680 Cells
Beyond structural innovation, Tesla’s development of the 4680 battery cells for the Cybertruck has been essential in lowering costs and enhancing performance. These 4680 cells, measuring 46 mm in diameter and 80 mm in length, offer a unique blend of efficiency and power. Their larger size compared to previous 2170 or 18650 cells means that fewer batteries are required to deliver the same energy capacity, which reduces the complexity and cost of the battery system.

Tesla’s 4680 cells feature a tabless design and utilize a cell-to-pack architecture, where the cells are directly integrated into the vehicle’s structure rather than housed in separate modules. This integration reduces the need for additional battery enclosures, cutting material costs and overall vehicle weight. The epoxy used to fill gaps around the cells also contributes to a rock-solid structure, making the battery pack both a power source and a critical structural component. This innovative approach reduces costs per kilowatt-hour by an estimated 56%, thanks to streamlined assembly and fewer materials required.
The 4680 cell design also addresses heat management more effectively, ensuring better battery longevity and efficiency under high load. Tesla’s structural integration of the battery not only cuts down on material and labor costs but also simplifies manufacturing, making the 4680 cells easier and faster to produce. This advancement in battery technology contributes significantly to the Cybertruck’s profitability by optimizing both performance and cost-efficiency.
5. Ultra-Hard 30X Cold-Rolled Stainless Steel: Innovation in Durability and Cost Savings
A final factor in Tesla’s ability to achieve rapid positive gross margin for Cybertruck manufacturing is the use of ultra-hard 30x cold-rolled stainless steel, also known as 300-series stainless steel, for its exoskeleton. This proprietary alloy offers unparalleled strength and durability, and it forms the Cybertruck’s iconic, rugged exterior.
Tesla’s choice of this stainless steel provides significant cost advantages. The flat panels and straight lines eliminate the need for costly stamping dies, blanking dies, and even traditional tooling, such as hemming dies, which would otherwise be required to shape and finish complex body panels. This reduction in manufacturing steps directly translates into savings on production costs.
Furthermore, Tesla’s first-principles approach allows them to bypass the need for a paint shop entirely. Typical vehicles require protective coatings and paint, which can wear off over time due to exposure to dust, scratches, and environmental factors. In contrast, the Cybertruck’s stainless steel exterior is corrosion-resistant, eliminating the need for additional coatings and simplifying the manufacturing process. By forgoing paint, Tesla saves significantly on production expenses and creates a more environmentally friendly production process.
This ultra-durable exoskeleton also serves as a powerful marketing tool. Its bulletproof and scratch-resistant qualities, famously demonstrated on platforms like the Joe Rogan podcast, showcase the vehicle’s resilience and aesthetic appeal. Celebrities and high-profile figures have shown interest in the Cybertruck not only for its functionality but for its eye-catching design, providing Tesla with valuable free publicity. Tesla’s choice of stainless steel is a testament to its focus on cost efficiency, durability, and appeal, driving high demand and contributing to its positive gross margin .
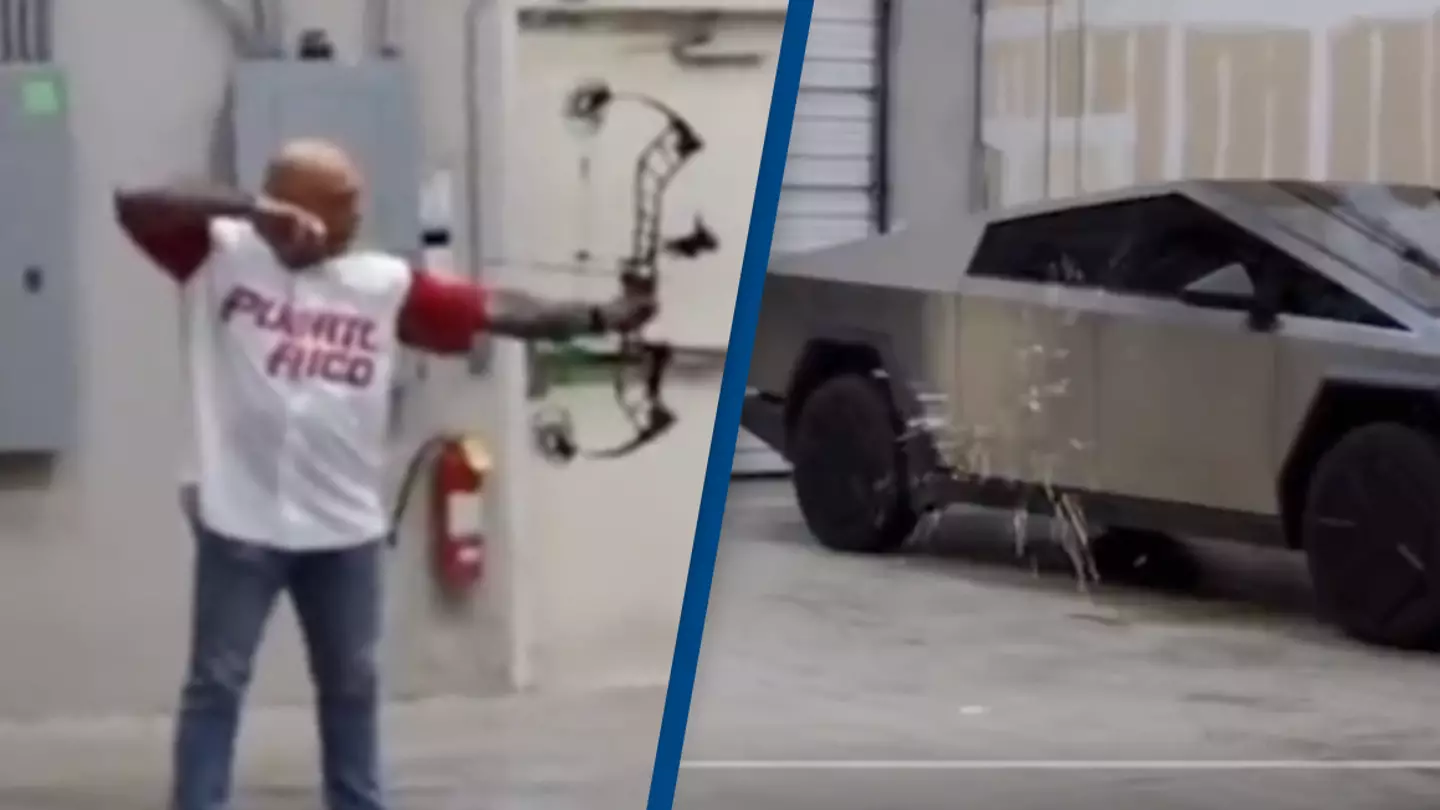

Joe Rogan attempted to shoot an arrow to pierce through the bulletproof cybertruck.
Conclusion
Tesla’s approach to the Cybertruck—from its revolutionary gigacasting and exoskeleton design to the integration of 4680 battery cells, Foundation Series pricing, and ultra-hard 30x stainless steel—showcases the company’s ability to push boundaries and redefine industry standards. Each innovation contributes not only to cost savings and production efficiency but also to the overall strength and appeal of the Cybertruck. As Tesla continues to refine its manufacturing processes, it sets a new benchmark for financial performance in the electric vehicle market. The Cybertruck is more than just a striking vehicle; it’s a testament to Tesla’s dedication to innovation, efficiency, and profitability.

